What is Systems Engineering
System engineering is a process used to design, build, and manage complex systems.
It involves the use of interdisciplinary approaches to ensure that a system is built and operates as intended. System engineering is an important skill for developers to know because it helps them to design and build software that is reliable, scalable, and efficient.
In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at system engineering, why it matters for developers, and how it relates to CI/CD tools and processes.
The Main Points of System Engineering
System engineering involves several key steps, including:
-
Requirements analysis: identifying the needs and requirements of the system, and translating them into design specifications.
-
Design: creating a detailed plan for how the system will be built, including hardware, software, and other components.
-
Implementation: building and testing the system according to the design specifications.
-
Verification and validation: testing the system to ensure that it meets the requirements and functions as intended.
-
Operation and maintenance: managing the system over its lifecycle, including maintenance, upgrades, and improvements.
Why System Engineering Matters for Developers
System engineering is important for developers because it helps them to design and build software that is reliable, scalable, and efficient. By using a structured approach to software development, developers can ensure that the software they build meets the needs and requirements of the system, and functions as intended.
This is particularly important for complex systems, where even small errors or inefficiencies can have significant impacts on performance and reliability.
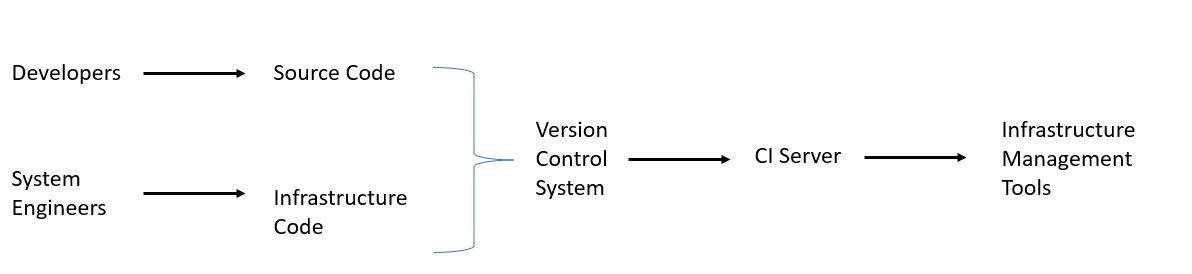
System Engineering and Infrastructure Management
System engineering is closely related to infrastructure management, which involves the design, deployment, and management of the hardware and software infrastructure required to support a system.
System engineering provides a structured approach to designing and building systems, while infrastructure management provides a structured approach to deploying and managing the hardware and software infrastructure that supports those systems.
Together, these two disciplines help to ensure that systems are designed, built, and managed in a way that meets the needs and requirements of the organization.
Infrastructure Workflow
-
Manual
-
Automatic
-
Declarative: Defines WHAT
-
Imperative: Defines HOW
CI/CD Tools and Processes
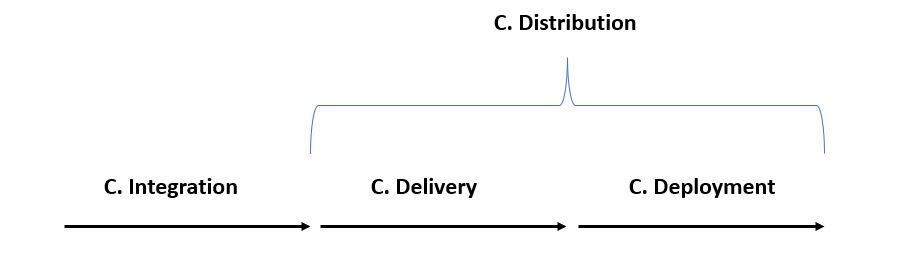
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery, and refers to a set of practices and tools used to automate and streamline the software development process.
CI/CD helps developers to deliver high-quality software more quickly and efficiently by automating the build, test, and deployment processes. The key sub-steps of CI/CD include:
-
Continuous Integration: automatically building and testing software as changes are made to the codebase.
-
Continuous Delivery: automatically deploying software to production or staging environments.
-
Continuous Deployment: automatically deploying software to production environments.
Popular CI/CD Tools
There are several popular CI/CD tools available, they will make easier than ever for developers to automate and streamline the software development process, and to deliver software that meets the needs of their users.
-
Jenkins: an open-source automation server that supports the entire CI/CD pipeline, from building and testing to deployment and monitoring.
-
Ansible: a popular automation tool that simplifies configuration management, application deployment, and task automation.
-
GitHub Actions: a powerful CI/CD tool built into the GitHub platform that allows developers to automate their workflows and build, test, and deploy software directly from GitHub.
Popular Infrastructure Provisioning Tools
-
Terraform: Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code (IaC) tool that allows users to define and provision infrastructure resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and networks, in a declarative way. Terraform can be used with a variety of cloud providers, including AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, and is well-suited for managing complex, multi-cloud environments.
-
Ansible: Ansible is an open-source configuration management tool that automates software provisioning, configuration management, and application deployment. Ansible uses a declarative language to define system configurations and deploys software using SSH or other remote protocols. Ansible can be used for a variety of use cases, from simple configuration management to complex orchestration of multi-tier applications.
-
Chef: Chef is an open-source configuration management tool that allows users to define and deploy software and infrastructure configurations across large, heterogeneous environments. Chef uses a declarative language to define system configurations and can be used to manage applications, databases, and middleware, as well as underlying infrastructure resources.
-
Puppet: Puppet is an open-source configuration management tool that automates the provisioning, configuration, and management of infrastructure resources. Puppet uses a declarative language to define system configurations and can be used to manage a variety of infrastructure resources, including servers, networks, and storage.
-
CloudFormation: CloudFormation is a provisioning tool provided by AWS that allows users to define and deploy infrastructure resources in a declarative way. CloudFormation uses templates to define infrastructure resources, such as EC2 instances, security groups, and load balancers, and can be used to manage a variety of AWS resources.
These tools are designed to simplify the process of provisioning and managing infrastructure resources, and can be used for a variety of use cases, including:
- Automating the deployment and management of complex, multi-tier applications
- Provisioning and configuring infrastructure resources in a declarative way
- Managing and maintaining infrastructure resources at scale
- Enforcing consistent configurations across large, heterogeneous environments
- Integrating with other tools and processes, such as CI/CD pipelines, to automate the delivery of software and infrastructure resources
Take Aways
System engineering is an important skill for developers to know because it helps them to design and build software that is reliable, scalable, and efficient. By using a structured approach to software development and integrating CI/CD tools and processes, developers can deliver high-quality software more quickly and efficiently, and ensure that their software meets the needs and requirements of the system.
Infrastructure provisioning tools can be a valuable resource for managing and maintaining infrastructure resources at scale, and can help to simplify the process of deploying and managing complex, multi-tier applications. By using these tools, developers and system administrators can reduce manual intervention, enforce consistent configurations, and automate the delivery of software and infrastructure resources.